Considering that up until about 85 years ago, cannabis oil was used around the world to treat a variety of diseases, including cancer, it is not surprising that the phasing out of cannabis to treat illness coincided with the rise of pharmaceutical companies.
Rick Simpson, a medical marijuana activist, is on a crusade to help others heal. He regards cannabis as the most medicinally active plant on the face of the earth, and shared this apparent miracle with others — completely free of charge. He now has thousands of testimonials from those who were healed from ‘incurable’ disease to back up his claims ~ that cannabis annihilates cancer.
For the naysayers out there who are still not convinced about the effectiveness of cannabis for curing cancer, the astounding healing attributes of the plant are well documented by a wealth of peer-reviewed studies.
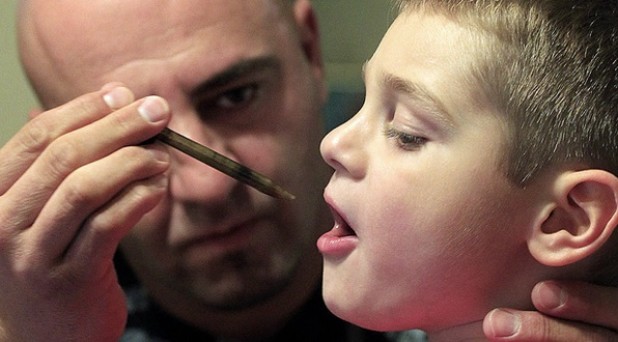
Traditional medicinal plant backed by modern medicine
Breast cancer
A study in Molecular Cancer Therapeutics explored the relationship between the use of cannabidiol (CBD) and the subsequent down regulation of breast cancer tumor aggressiveness. The researchers concluded that CBD represents the first nontoxic agent to decrease the aggressiveness of metastatic breast cancer cells in vivo.
Several additional studies support these findings, including “Pathways mediating the effects of cannabidiol on the reduction of breast cancer cell proliferation, invasion and metastasis” and “Cannabinoids: a new hope for breast cancer therapy?”
Furthermore, the journal PLoS One reports further evidence of how cannabinoids modulate breast cancer tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting specific receptors.
Colon cancer
As published in Pharmacological Research:
“Studies on epithelial cells have shown that cannabinoids exert antiproliferative, antimetastatic and apoptotic effects as well as reducing cytokine release and promoting wound healing. In vivo, cannabinoids – via direct or indirect activation of CB(1) and/or CB(2) receptors – exert protective effects in well-established models of intestinal inflammation and colon cancer.”
The team concluded that the administration of cannabinoids “may be a promising strategy to counteract intestinal inflammation and colon cancer.”
Moreover, research in the Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology established that colon cancer cell lines were strongly affected by cannabinoids.
Leukemia
Cannabis was shown to induce cytotoxicity in leukemia cell lines, according the the journal Blood:
“We have shown that THC is a potent inducer of apoptosis, even at 1 x IC(50) (inhibitory concentration 50%) concentrations and as early as 6 hours after exposure to the drug. These effects were seen in leukemic cell lines (CEM, HEL-92, and HL60) as well as in peripheral blood mononuclear cells.”
It also did not appear that the cannabis was simply aiding other chemo drugs — it was independently bringing about results with the active compound THC responsible for cancer cell death in vitro.
Likewise, a study in the Molecular Pharmacology Journal found that non psychoactive cannabidiol dramatically induced apoptosis (cell death) in leukemia cells. “Together, the results from this study reveal that cannabidiol, acting through CB2 and regulation of Nox4 and p22(phox) expression, may be a novel and highly selective treatment for leukemia.”
Two additional studies, “p38 MAPK is involved in CB2 receptor-induced apoptosis of human leukemia cells” and “Gamma-irradiation enhances apoptosis induced by cannabidiol, a non-psychotropic cannabinoid, in cultured HL-60 myeloblastic leukemia cells“, also demonstrated the effectiveness of cannabis in promoting leukemia cell death.
Immunity
Research published in the paper Prostaglandins, Leukotrienes and Essential Fatty Acids found that cannabinoid compounds play a vital role in modulating the immune system to improve the outcome of a cancer diagnosis. In short, the team believes “[t]he experimental evidence reviewed in this article argues in favor of the therapeutic potential of these compounds in immune disorders and cancer.”
Moreover, the study Cannabinoids and the immune system confirms that cannabimimetic agents have substantial effects on natural killer cells, thereby providing therapeutic usefulness in reducing tumor growth and the induction of apoptosis. Therefore, cannabis demonstrates a “subtle but significant role in the regulation of immunity and that this role can eventually be exploited in the management of human disease.”
Cervical cancer
Uterine cervical cancer cells are significantly influenced by cannabis as well. Published in Gynecologic Oncology, the research team discovered that the compound induced apoptosis in cervical carcinoma (CxCa) cell lines.
Melanoma
The most deadly form of skin cancer, melanoma has relatively few options of treatment beyond prevention and early detection. With this in mind, the findings of the study Cannabinoid receptors as novel targets for the treatment of melanoma are of particular note. In animal tests, cannabinoids encouraged cancer cell death, while decreasing growth, proliferation and metastasis of melanoma cells.
Non melanoma skin cancers also respond well to cannabinoids. According to research in the Journal of Clinical Investigation:
“Local administration of [cannabinoids] induced a considerable growth inhibition of malignant tumors generated by inoculation of epidermal tumor cells into nude mice. Cannabinoid-treated tumors showed an increased number of apoptotic cells. This was accompanied by impairment of tumor vascularization, as determined by altered blood vessel morphology and decreased expression of proangiogenic factors (VEGF, placental growth factor, and angiopoietin 2). … These results support a new therapeutic approach for the treatment of skin tumors.”
These are just a few examples — among hundreds — that demonstrate the effectiveness of cannabis in eradicating cancer without adverse side-effects. Additionally, the following documentary explores the history and modern uses of cannabis to heal serious diseases such as cancer, AIDS, Crohn’s disease & more:
Medical Cannabis and Its Impact on Human Health: a Cannabis Documentary
Scientific Studies from the National Institute of Health
If you’re still in doubt regarding the effectiveness of cannabis for healing cancer, have a look at these 100+ scientific studies from the National Institute of Health:
Cannabis kills tumor cells
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1576089
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20090845
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/616322
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14640910
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19480992
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15275820
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15638794
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16818650
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17952650
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20307616
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16616335
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16624285
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10700234
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17675107
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14617682
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17342320
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16893424
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15026328
Uterine, testicular, and pancreatic cancers
- http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/pdq/cam/cannabis/healthprofessional/page4
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20925645
Brain cancer
Mouth and throat cancer
Breast cancer
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18454173
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16728591
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9653194
Lung cancer
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/25069049
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22198381?dopt=Abstract
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21097714?dopt=Abstract
Prostate cancer
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12746841?dopt=Abstract
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3339795/?tool=pubmed
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22594963
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15753356
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10570948
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19690545
Blood cancer
Skin cancer
Liver cancer
Cannabis cancer cures (general)
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12514108
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15313899
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20053780
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18199524
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19589225
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12182964
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19442435
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12723496
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16250836
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17237277
Cancers of the head and neck
Cholangiocarcinoma cancer
Leukemia
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15454482
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16139274
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14692532
Cannabis partially/fully induced cancer cell death
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12130702
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19457575
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18615640
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17931597
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18438336
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19916793
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18387516
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15453094
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19229996
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9771884
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18339876
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12133838
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16596790
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11269508
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15958274
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19425170
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17202146
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11903061
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15451022
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20336665
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19394652
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11106791
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19189659
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16500647
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19539619
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19059457
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16909207
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18088200
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10913156
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18354058
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19189054
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17934890
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16571653
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19889794
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15361550
Translocation-positive rhabdomyosarcoma
Lymphoma
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18546271
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16936228
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16337199
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19609004
Cannabis kills cancer cells
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16818634
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12648025
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17952650
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16835997
Melanoma
Thyroid carcinoma
Colon cancer
Intestinal inflammation and cancer
Cannabinoids in health and disease
Cannabis inhibits cancer cell invasion
Courtesy of Wake Up World contributor Carolanne Wright